Managing money wisely is the foundation of financial stability. When it comes to storing and growing your money, the two most popular options are a savings account and a fixed deposit (FD). Both are considered safe, reliable, and widely used by individuals who want to save while earning interest.
But the big question is: How to choose between a savings account and a fixed deposit? Let’s explore their features, differences, benefits, and which one might be the right choice for your financial goals.
What is a Savings Account?
A savings account is a deposit account offered by banks and credit unions that allows individuals to deposit money, earn interest, and withdraw funds easily.
- Provides high liquidity—you can access funds anytime.
- Usually offers lower bank interest rates compared to fixed deposits.
- Best suited for day-to-day banking and emergency funds.
Important: A savings account is ideal if you want flexibility and easy access to your money.
What is a Fixed Deposit (FD)?
A fixed deposit account is a financial product where you deposit a lump sum for a specific period at a predetermined interest rate.
- Higher bank interest rates than savings accounts.
- Limited liquidity—you cannot withdraw without penalty before maturity.
- Considered a safe investment option for long-term financial planning.
Important: A fixed deposit is best if your goal is to grow money safely over a fixed time horizon.
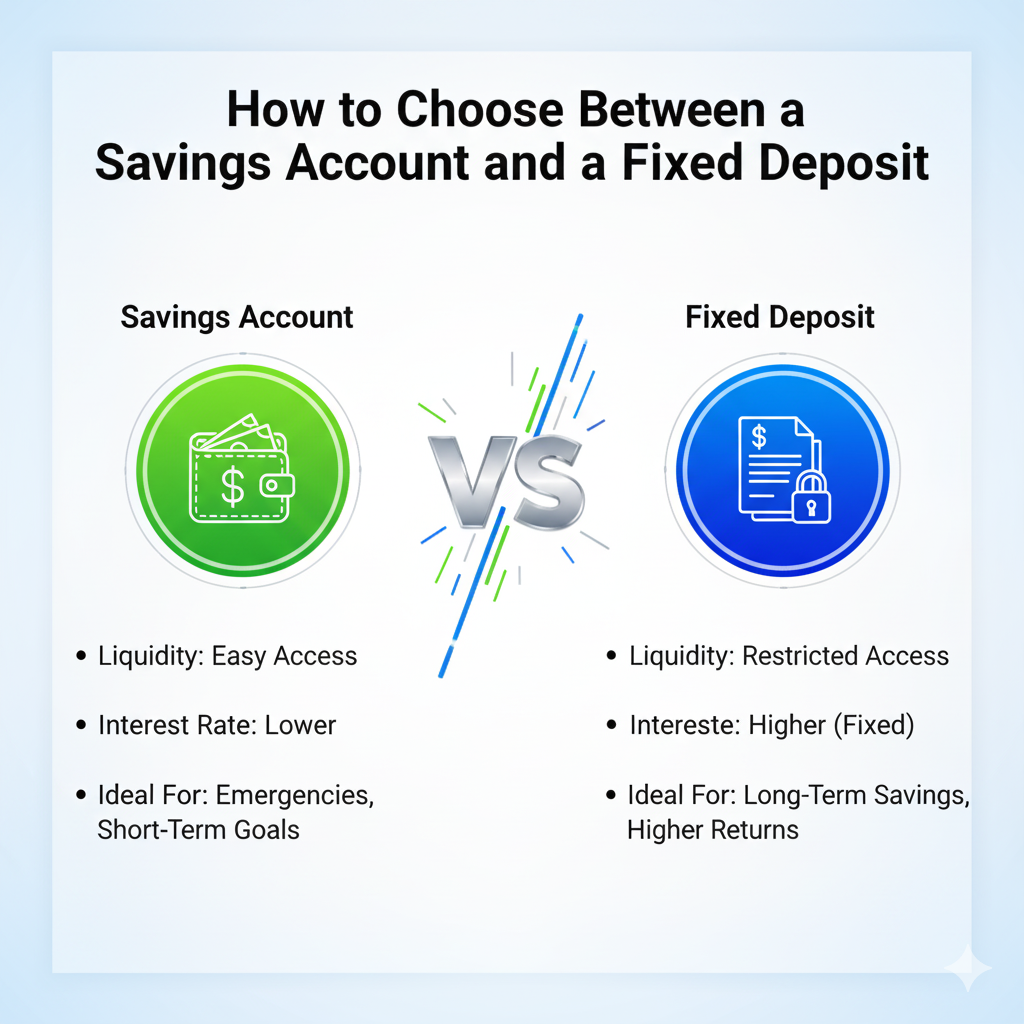
Key Differences Between Savings Account and Fixed Deposit
When deciding how to choose between a savings account and a fixed deposit, understanding their differences is crucial:
| Feature | Savings Account | Fixed Deposit |
|---|---|---|
| Liquidity | High – withdraw anytime | Low – locked until maturity |
| Interest Rates | Lower | Higher |
| Financial Planning | Short-term, daily needs | Long-term, wealth growth |
| Safety | Safe investment, but lower returns | Safe investment with stable returns |
| Tax Implications | Minimal | Interest may be taxable if above limits |
Key takeaway: Choose based on whether you prioritize liquidity or higher returns.
When to Choose a Savings Account
A savings account is better suited when:
- You need frequent access to your money.
- You are building an emergency fund.
- You prefer flexibility over fixed returns.
- Your financial planning includes short-term goals like bill payments or daily expenses.
Important: If you value quick withdrawals and easy banking, a savings account is your best choice.
When to Choose a Fixed Deposit
A fixed deposit is more suitable when:
- You want to earn higher returns without taking risks.
- You don’t need immediate access to your funds.
- You are planning for medium to long-term goals such as vacations, education, or retirement.
- You want a safe investment with guaranteed returns.
Important: If your money can stay locked in, a fixed deposit will reward you with better interest earnings.
Pros and Cons of Savings Accounts
✅ Pros:
- Easy withdrawals and deposits
- Online and mobile banking facilities
- Useful for short-term needs and daily expenses
❌ Cons:
- Lower bank interest rates
- Limited potential for wealth growth
Pros and Cons of Fixed Deposits
✅ Pros:
- Higher returns compared to savings accounts
- A safe investment with guaranteed maturity value
- Encourages disciplined savings
❌ Cons:
- Limited liquidity (penalties for early withdrawal)
- Interest income may be taxable
How to Decide: Savings Account vs Fixed Deposit
When making a decision on how to choose between a savings account and a fixed deposit, consider the following factors:
- Your Financial Goals – For daily expenses, choose savings. For long-term growth, choose fixed deposit.
- Liquidity Needs – Do you need quick access to money or can you lock it away?
- Bank Interest Rates – Compare rates offered by different institutions.
- Risk Appetite – Both are safe, but savings accounts are more flexible, while FDs guarantee higher returns.
- Tax Planning – Factor in how the interest earned affects your taxable income.
Important: There is no “one-size-fits-all” answer—your choice depends on your personal financial planning strategy.
Balanced Approach: Combining Both
The smartest option for many individuals is to maintain both a savings account and a fixed deposit.
- Keep a portion of funds in a savings account for emergencies and regular use.
- Place surplus funds in a fixed deposit to earn higher returns.
This combination ensures liquidity + wealth growth, supporting both short-term and long-term goals.
Final Thoughts
Deciding how to choose between a savings account and a fixed deposit ultimately depends on your financial needs.
- If you prioritize liquidity and flexibility, a savings account is best.
- If you want higher interest rates and disciplined saving, a fixed deposit is the right choice.
Important: For most people, a mix of both is the ideal financial planning strategy—secure, safe investment with easy access when needed.
✅ In summary: Both savings accounts and fixed deposits are valuable tools. Your decision should align with your financial goals, liquidity needs, and risk tolerance.
 English
English
 简体中文
简体中文
 العربيّة
العربيّة